Questions
Solutions for each problem can be found at the bottom of this page.
Conceptual Questions
- A class definition provides a pattern for creating objects, but doesn’t make any objects itself. (T/F)
- By convention, Python class names start with a lowercase letter. (T/F)
- When you define a method in a class, all objects of that class have that method associated with it. (T/F)
- The first parameter of a method is a copy of the object the method is called on. (T/F)
- A class definition must come before an object of that class is instantiated. (T/F)
- You must have an instance of a class (an object) to call the class’s constructor. (T/F)
- Constructors must have the
selfparameter in their signature. (T/F) - Constructors must take at least one parameter other than the self parameter. (T/F)
- Objects are passed into functions by reference. (T/F)
- The type of an object is the same as the name of the class it is an instance of. (T/F)
Memory Diagrams
- Produce a memory diagram for the following code snippet, being sure to include its stack and output.
class Point:
"""Models the idea of a point at location (x, y)."""
x: int
y: int
def __init__(self, x: int, y: int):
"""Constructor definition!"""
self.x = x
self.y = y
class Path:
"""Models the idea of a path from point a to point b."""
a: Point
b: Point
def __init__(self, a: Point, b: Point):
"""Constructor definition!"""
self.a = a
self.b = b
def scale(self, amount: int) -> None:
"""Scales the points by a specified amount."""
self.a.x *= amount
self.b.y *= amount
def translate(self) -> None:
"""Moves the points up 2 units and right 5 units."""
self.a.x += 5
self.a.y += 2
self.b.x += 5
self.b.y += 2
def main() -> None:
"""Entrypoint of the program."""
p1: Point = Point(2, 1)
p2: Point = Point(3, 6)
line1: Path = Path(p1, p2)
line2: Path = line1
line2.translate()
line2.scale(2)
print(f"{line1.a.x} , {line1.a.y}")
print(f"{line2.a.x} , {line2.a.y}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
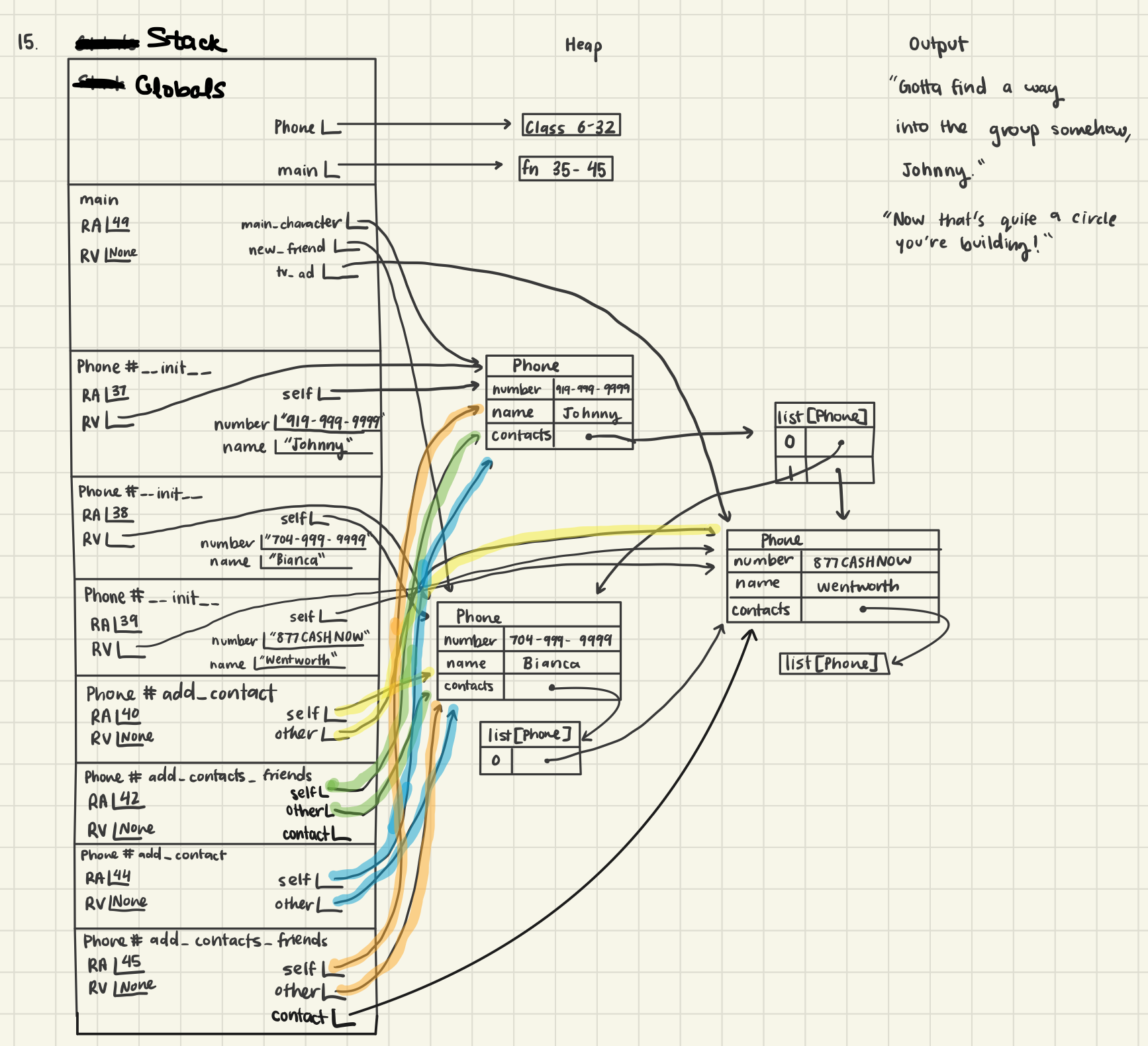
main()- Produce a memory diagram for the following code snippet, being sure to include its stack and output.
"""Diagramming practice for Quiz 03."""
from __future__ import annotations
class Phone:
"""Represents a phone as a class."""
number: str
name: str
contacts: list[Phone]
def __init__(self, number: str, name: str):
"""Creates a phone object."""
self.number = number
self.name = name
self.contacts = []
def add_contact(self, other: Phone) -> None:
"""Making friends!"""
if not (other in self.contacts):
self.contacts.append(other)
def add_contacts_friends(self, other: Phone) -> None:
"""A friend introduces you to a new friend group :D."""
if other in self.contacts:
print("Now that's quite a circle you're building!")
for contact in other.contacts:
if not (contact in self.contacts):
self.contacts.append(contact)
else:
print(f"Gotta find a way into the group somehow, {self.name}.")
def main():
"""Entrypoint into the program."""
main_character: Phone = Phone("919-999-9999", "Johnny")
new_friend: Phone = Phone("704-999-9999", "Bianca")
tv_ad: Phone = Phone("877CASHNOW", "Wentworth")
new_friend.add_contact(tv_ad)
main_character.add_contacts_friends(new_friend)
main_character.add_contact(new_friend)
main_character.add_contacts_friends(new_friend)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()- Produce a memory diagram for the following code snippet, being sure to include its stack and output.
"""From number grades to letters."""
def main() -> None:
"""The entrypoint of the program."""
student_grades: dict[str, int] = {"Andre": 92, "Jonny": 79, "Ania": 86, "Wendy": 55}
curve(student_grades)
letter_grades: dict[str, str] = grading_scale(student_grades)
print(letter_grades)
def curve(number_grades: dict[str, int]) -> None:
"""Curves number grades."""
max: int = 0
for student in number_grades:
if number_grades[student] > max:
max = number_grades[student]
curve_amount: int = 100 - max
for student in number_grades:
number_grades[student] += curve_amount
def grading_scale(number_grades: dict[str, int]) -> dict[str, str]:
"""Converts grades formatted as numbered into letter grades."""
gradebook: dict[str, str] = {}
for student in number_grades:
if number_grades[student] >= 90:
gradebook[student] = "A"
elif number_grades[student] >= 80:
gradebook[student] = "B"
elif number_grades[student] >= 70:
gradebook[student] = "C"
elif number_grades[student] >= 60:
gradebook[student] = "D"
else:
gradebook[student] = "F"
return gradebook
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()Please check the practice memory diagram page for more practice!
Class Writing
- This class is slightly challenging, but take it step by step! Create a
ChristmasTreeFarmclass with the following specifications:- The
ChristmasTreeFarmclass should have one attribute: alist[int]namedplots.- Basic behavior of
plots(you will define this later):- This list will hold values that represent the size of the tree planted in each plot.
- If the value at an index of the list is 0, then the plot at that index is empty (does not have a tree).
- Any value other than 0 indicates that a tree is growing in that plot!
- Basic behavior of
- The constructor for the class should take two arguments:
plots: intandinitial_planting: int, both of type int.- The first parameter,
plots, represents the total number of plots in the farm. (Notice that the attributeplotsand the parameterplotsfor this constructor are different, and represent different things!) - The second parameter,
initial_planting, represents the number of plots that that will have trees already planted in them. These initially planted plots will be trees of size 1. - The constructor should initialize the
plotsattribute to an emptylist, and then appendinitial_plantingtrees of size 1. After that, the constructor should fill the rest of the plots with zeroes to indicate that they are empty!
- The first parameter,
- The class should define a method called
plant.- This method should have a parameter of type
int, representing the plot index at which a tree should be planted. - The tree should be size 1 when planted. If this method is called on a plot that already has a tree, the old tree will be uprooted and replaced with a new baby tree (size 1).
- This method should have a parameter of type
- The class should define a method called
growth.- This method should increase the size of each planted tree by 1. (Remember that unplanted plots are represented by a 0 in the
plotslist.)
- This method should increase the size of each planted tree by 1. (Remember that unplanted plots are represented by a 0 in the
- The class should define a method called
harvest.- This method should have a parameter
replantof typeboolthat will determine whether this method replants trees (sets them to size 1 after harvest) or leaves the plots empty (sets them to size 0 after harvest). - For this method, trees that are at least size 5 will be harvested. The method will
returnthe count of how many trees were successfully harvested (typeint).
- This method should have a parameter
- The class should overload the addition operator.
- This method should work between two objects of type
ChristmasTreeFarm. - The method should return a new
ChristmasTreeFarmobject whose size is the sum of the givenChristmasTreeFarm’s, and whose initial plantings are the sum of the number of planted trees in the givenChristmasTreeFarms.
- This method should work between two objects of type
- Check your code: If you want to check and see if your code works, you can use the autograder. Check out the instructions below to join the autograder Gradescope if you haven’t yet. (It’s the same one used for QZ02 practice!) For the autograder to work, you need to save your file in your lessons folder, in a folder called “practice” and in a file called “tree_farm.py”. Create the zip folder by running the command:
python -m tools.submission lessons/practice
- The
Function Writing
- Write a function called
find_courses. Given the followingCourseclass definition,find_coursesshould take in alist[Courses]and astrprerequisite to search for. The function should return a list of thenamesof each Course whoselevelis 400+ and whoseprerequisiteslist contains the given string.
class Course:
"""Models the idea of a UNC course."""
name: str
level: int
prerequisites: list[str]Write a method called
is_valid_coursefor theCourseclass. The method should take in astrprerequisite and return aboolthat represents whether the course’slevelis 400+ and if itsprerequisiteslist contains the given string.Check your code: If you want to check and see if your code works, you can use the autograder. Check out the instructions below to join the autograder Gradescope if you haven’t yet. (It’s the same one used for QZ02 practice!) For the autograder to work, you need to save your file in your lessons folder, in a folder called “practice” and in a file called “courses.py”. Create the zip folder by running the command: `python -m tools.submission lessons/practice
Autograder Instructions
Join the Gradescope class for practice problems with the code: 4V7PB5 (Do this by going to your Gradescope homepage and clicking on “Enroll in Course”) Do not compress these files before submitting. Simply submit the .py files.
Solutions
Conceptual Questions
- True
- False
- True
- False
- True
- False
- True
- False
- True
- True
Memory Diagrams
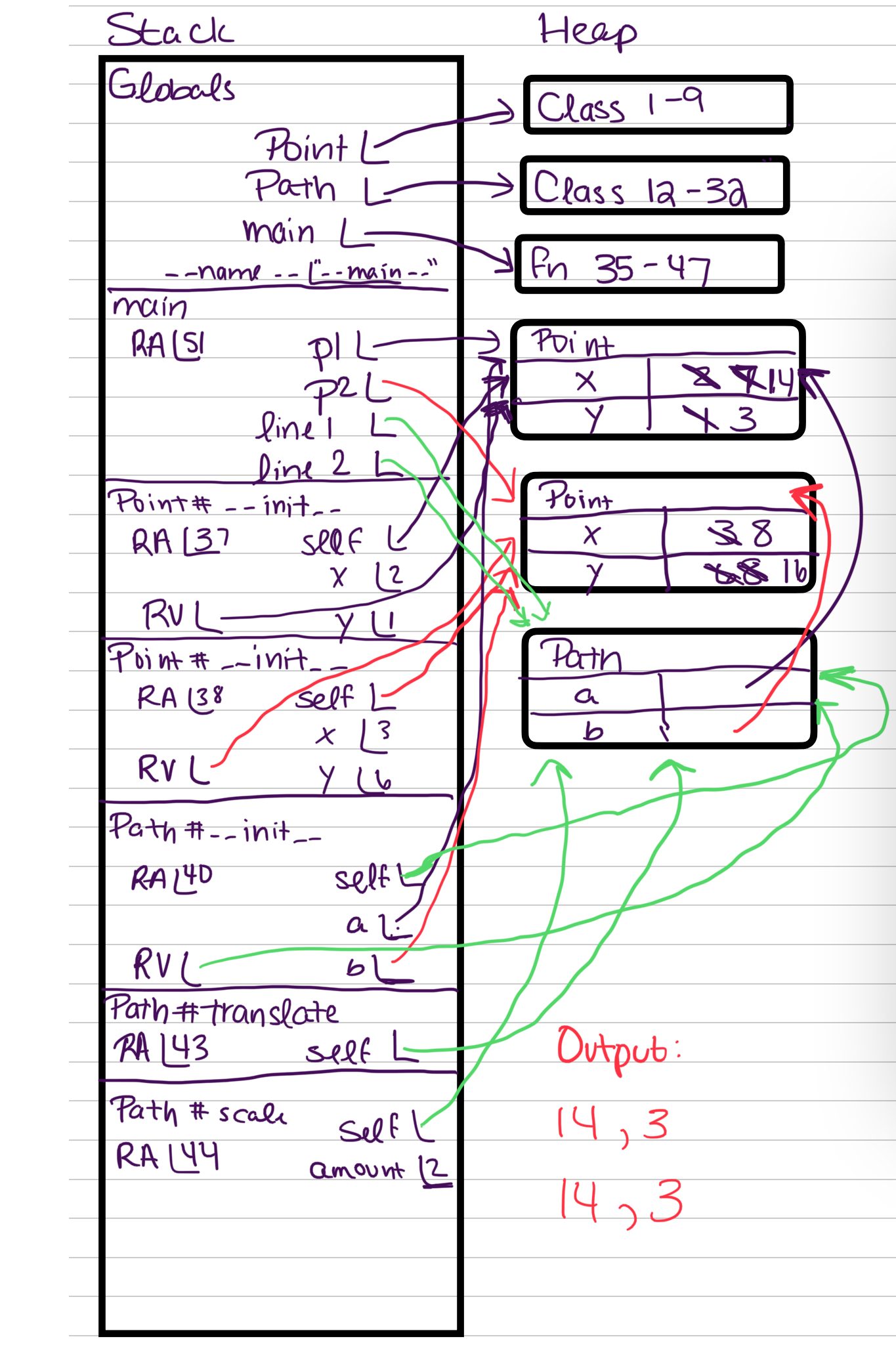
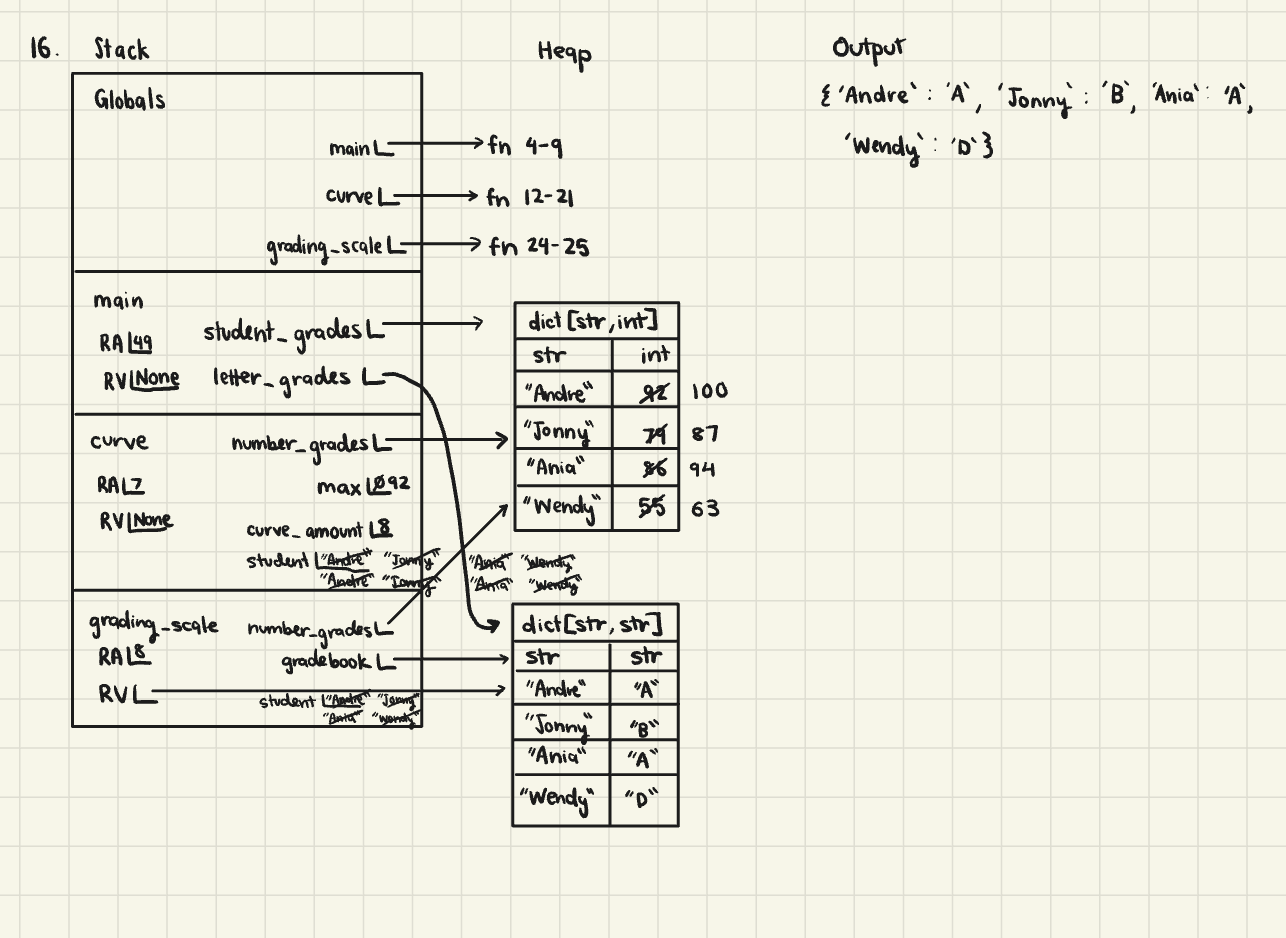
Class Writing
"""Diagraming practice for Quiz 03."""
class ChristmasTreeFarm:
"""A christmas tree farm!"""
plots: list[int]
def __init__(self, plots: int, initial_planting: int) -> None:
"""Sets up the farm."""
self.plots = []
i: int = 0
while i< initial_planting:
self.plots.append(1)
i += 1
while i < plots:
self.plots.append(0)
i += 1
def plant(self, plot_number: int) -> None:
"""Plants a tree at the given plot number."""
self.plots[plot_number] = 1
def growth(self) -> None:
"""Grows each planted tree."""
i: int = 0
while i < len(self.plots):
if self.plots[i] != 0:
self.plots[i] += 1
i += 1
def harvest(self, replant: bool) -> int:
"""Harvest trees that are fully grown!"""
total: int = 0
i: int = 0
while i < len(self.plots):
if self.plots[i] >= 5:
total += 1
if replant:
self.plots[i] = 1
else:
self.plots[i] = 0
i += 1
return total
def __add__(self, rhs: ChristmasTreeFarm) -> ChristmasTreeFarm:
"""Overload addition to create new ChristmasTreeFarm."""
trees: int = 0
for plot in self.plots:
if plot > 0:
trees += 1
for plot in rhs.plots:
if plot > 0:
trees += 1
return ChristmasTreeFarm(len(self.plots) + len(rhs.plots), trees)Function Writing
def find_courses(courses: list[Course], prereq: str) -> list[str]:
"""Finds 400+ level courses with the given prereq."""
results: list[str] = []
for c in courses:
if c.level >= 400:
for p in c.prerequisites:
if p == prereq:
results.append(c.name)
return results def is_valid_course(self, prereq: str) -> bool:
"""Checks if this course is 400+ level and has the given prereq."""
if self.level < 400:
return False
else:
for p in self.prerequisites:
if p == prereq:
return True
return False